Android使用include/merge/ViewStub优化布局
一、使用include标签将可复用的组件抽取出来(引用布局)
二、使用merge标签减少布局的嵌套层次(merge相当于framelayout)
场景1:布局根结点是FrameLayout且不需要设置background或padding等属性,可以用merge代替。
场景2:某布局作为子布局被其他布局include时,使用merge当作该布局的顶节点,这样在被引入时,顶结点会自动被忽略。
三、使用ViewStub标签来加载一些不常用的布局
作用:ViewStub标签同include标签一样可以用来引入一个外部布局,不同的是,ViewStub引入的布局默认不会扩张,既不会占用显示也不会占用位置,从而在解析Layout时节省cpu和内存
示例一:include

下面是res/layout/title.xml 布局文件:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/title_bg" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/title_back"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="@drawable/back_bg"
android:text="Back"
android:textColor="#fff" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title_text"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="This is Title"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="25sp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/title_edit"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:background="@drawable/edit_bg"
android:text="Edit"
android:textColor="#fff" />
下面是res/layout/activity_main.xml 布局文件:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
示例二:merge
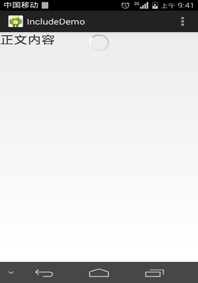
下面是res/layout/progress.xml 布局文件:
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center" />
下面是res/layout/activity_main.xml 布局文件:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="正文内容"
android:textSize="25sp" />
示例三:ViewStub

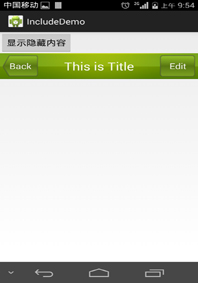
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="显示隐藏内容"/>
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/id_viewStub"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout="@layout/title"/>
下面是MainActivity.java主界面文件:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button b;
private ViewStub stub;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
b=(Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
stub=(ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.id_viewStub);
b.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
stub.inflate();
}
});
}
}
用户界面View之Dialog 对话框
一、AlertDialog常用方法
使用AlertDialog.Builder中的create()方法创建一个AlertDialog
setTitle();给对话框设置标题
setIcon();给对话框设置图标
setMessage();设置对话框的提示信息
setView() 给对话框设置自定义样式
setItems();设置对话框要显示的一个list,一般用于显示几个命令时
setSingleChoiceItems();设置对话框显示一个单选的List
setMultiChoiceItems();设置对话框显示一系列的复选框
setNeutralButton();普通按钮
setPositiveButton();给对话框添加"确定"按钮
setNegativeButton();给对话框添加"取消"按钮
示例一:


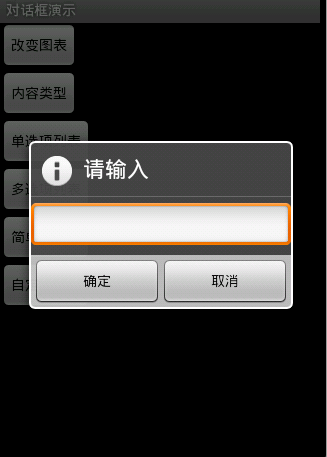
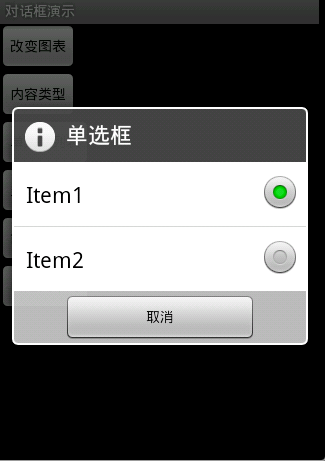
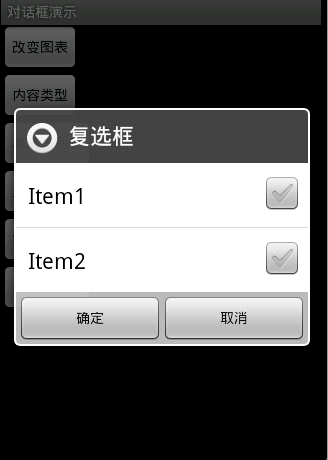

图1效果:该效果是当按返回按钮时弹出一个提示,来确保无误操作,采用常见的对话框样式。
代码:
创建对话框方法dialog()
protected void dialog() {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new Builder(Main.this);
builder.setMessage("确认退出吗?");
builder.setTitle("提示");
builder.setPositiveButton("确认", new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
Main.this.finish();
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
builder.create().show();
}
在onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event)方法中调用此方法
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
if (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK && event.getRepeatCount() == 0) {
dialog();
}
return false;
}
图2效果:改变了对话框的图表,添加了三个按钮
Dialog dialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setIcon(
android.R.drawable.btn_star).setTitle("喜好调查").setMessage(
"你喜欢李连杰的电影吗?").setPositiveButton("很喜欢",
new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(Main.this, "我很喜欢他的电影。",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}).setNegativeButton("不喜欢", new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(Main.this, "我不喜欢他的电影。", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
}
}).setNeutralButton("一般", new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(Main.this, "谈不上喜欢不喜欢。", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
.show();
}
}).create();
dialog.show();
图3效果:信息内容是一个简单的View类型
new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setTitle("请输入").setIcon(
android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_info).setView(
new EditText(this)).setPositiveButton("确定", null)
.setNegativeButton("取消", null).show();
图4效果:信息内容是一组单选框
new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setTitle("复选框").setMultiChoiceItems(
new String[] { "Item1", "Item2" }, null, null)
.setPositiveButton("确定", null)
.setNegativeButton("取消", null).show();
图5效果:信息内容是一组多选框
new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setTitle("单选框").setIcon(
android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_info).setSingleChoiceItems(
new String[] { "Item1", "Item2" }, 0,
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
}).setNegativeButton("取消", null).show();
图6效果:信息内容是一组简单列表项
new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setTitle("列表框").setItems(
new String[] { "Item1", "Item2" }, null).setNegativeButton(
"确定", null).show();
图7效果:信息内容是一个自定义的布局
1.布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:background="#ffffffff" android:orientation="horizontal"
android:id="@+id/dialog">
<TextView android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tvname" android:text="姓名:" />
<EditText android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/etname" android:minWidth="100dip"/>
</LinearLayout>
2.调用代码
LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater();
View layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.dialog,
(ViewGroup) findViewById(R.id.dialog));
new AlertDialog.Builder(this).setTitle("自定义布局").setView(layout)
.setPositiveButton("确定", null)
.setNegativeButton("取消", null).show();
1、生成正式版本,并找到unsigned文件的路径,记下来
demo-unsigned.apk
2、用keytool生成签名keystore文件
keytool -genkey -v -keystore <keystoreName>.keystore -alias <Keystore AliasName> -keyalg <Key algorithm> -keysize <Key size> -validity <Key Validity in Days>
<keystoreName>:要生成的签名文件名,扩展名为 keystore
<Keystore AliasName>:签名的别名,作为唯一性依据
<Key algorithm>:加密方式,譬如RSA
<Key size>:签名长度,可忽略
<Key Validity in Days>:有效期,单位是 天
输入以上命令后,接下来按提示操作,分别是:
输入密码,
确认密码,
组织单位名称,
组织名称,
市,
省,
国家两字母代码(中国是CN)
最后,核对以上信息,按Y完成
输入主密码,这里我不是太了解为什么要分两个,直接回车表示使用相同密码。
3、用jarsigner给未签名的应用签名并生成已签名的应用
jarsigner -verbose -keystore <keystorename> -signedjar <Output Signed APK file> -digestalg SHA1 -sigalg MD5withRSA <Unsigned APK file> <Keystore Alias name>
<keystorename>:上一步通过keytool生成的签名文件(带扩展名keystore)
<Output Signed APK file>:签名后输出的文件
<Unsigned APK file>:未签名且此刻用于签名的文件
<Keystore Alias name>:签名的别名(不带扩展名keystore)
然后,按提示输入上一步设置的密码,即可大功告成。
关于keytool和jarsigner显示乱码的问题,解决方法
部分脚本在 MAC OS X 的终端输出不了正常中文,取而代之的是?,即乱码,原因是其编码不正确。本以为UTF-8可以打天下,谁知有人不按常理出牌,比如keytool和jarsigner。。。
解决方法:
打开终端后在菜单-偏好设置-描述文件-高级,下面有文本编码的设置,默认是UTF-8,这里我改为中文(GB 18030),至少keytool和jarsigner返回的中文可以正常显示。
注意:
不同的颜色风格自有一套高级选项,所以修改了文本编码后切换其他的颜色风格不会把该设置带过去
在网上找了很多关于dialog的自定义样式的问题,还有很多人写得比较复杂,需要改动style什么的,或者是自定义dialog搞得很复杂,我最后还是找到了方法来实现。
下面是我的dialog布局xml文件:
[mw_shl_code=java,true]<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/transparent"
android:layout_margin="50dp">
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/rl_dialog_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="@drawable/alertdialog_bg">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/dialog_text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="现在就打电话给客服:arjinmc"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:layout_marginRight="30dp"
android:maxLines="5"
android:gravity="center"
/>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/ll_buttons"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_margin="30dp">
<Button
android:id="@+id/dialog_cancel"
android:text="@string/alert_cancel"
android:background="@drawable/btn_long_white"
style="@style/dialog_button"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:textColor="@color/tabs_font"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/dialog_ok"
android:text="@string/alert_ok"
android:background="@drawable/btn_long_red"
style="@style/dialog_button"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"/>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/dialog_close"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/alertdialog_close"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
[/mw_shl_code]
在代码中需要这样写就可以了:
[mw_shl_code=java,true]//布局文件转换为view对象
LayoutInflater inflaterDl = LayoutInflater.from(this);
RelativeLayout layout = (RelativeLayout)inflaterDl.inflate(R.layout.layout_dialog, null );
//对话框
final Dialog dialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(SettingActivity.this).create();
dialog.show();
dialog.getWindow().setContentView(layout);
//取消按钮
Button btnCancel = (Button) layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_cancel);
btnCancel.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "cancel", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
//确定按钮
Button btnOK = (Button) layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_ok);
btnOK.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "ok", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
//关闭按钮
ImageButton btnClose = (ImageButton) layout.findViewById(R.id.dialog_close);
btnClose.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
});[/mw_shl_code]
非常easy!自己动手吧。
自定义dialog的样式并比较日期
<style name="myDialogTheme" parent="android:style/Theme.Dialog">
<item name="android:windowNoTitle">true</item>
</style>
1、布局main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:text="按下按钮试试"/>
</LinearLayout>
2、ly_dialogcontent
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="220dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#88E0EEEE">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:text="查询"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="10dp"
android:gravity="center">
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="开始时间:"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/beginTime"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:singleLine="true"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="10dp"
android:gravity="center">
<TextView
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="开始时间:"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/endTime"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:singleLine="true"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center">
<Button
android:id="@+id/search"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1.0"
android:text="查询"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/cancel"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1.0"
android:text="取消"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
3、Mainactivity
package com.ct.dialog;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.DatePickerDialog;
import android.app.DatePickerDialog.OnDateSetListener;
import android.app.Dialog;
import android.app.TimePickerDialog;
import android.app.TimePickerDialog.OnTimeSetListener;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.InputType;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.DatePicker;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TimePicker;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
private Button btnBn;
private Dialog dlg;
private LayoutInflater mInflater;
private Calendar calendar;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
btnBn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn);
init();
btnBn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
dlg.show();
}
});
}
private void init(){
calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
dlg = new Dialog(MainActivity.this, R.style.myDialogTheme);
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this);
dlg.setCancelable(true);
dlg.setCanceledOnTouchOutside(true);
View view = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.ly_dialogcontent, null);
final EditText begin = (EditText)view.findViewById(R.id.beginTime);
final EditText end = (EditText)view.findViewById(R.id.endTime);
Button sbtn = (Button)view.findViewById(R.id.search);
Button clebt = (Button)view.findViewById(R.id.cancel);
begin.setInputType(InputType.TYPE_NULL);
end.setInputType(InputType.TYPE_NULL);
dlg.setContentView(view);
//取消
clebt.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
dlg.dismiss();
}
});
//查询
sbtn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String beginTime = begin.getText().toString();
String endTime = end.getText().toString();
if (beginTime.equals("")|| endTime.equals("")) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "都不能为空", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}else if(!isLarge(beginTime, endTime)){
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "结束时间不能比开始时间小", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} else {
dlg.dismiss();}
}
});
//开始时间
begin.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
final String second = "00";
DatePickerDialog dpg = new DatePickerDialog(MainActivity.this,
new OnDateSetListener() {
@Override
public void onDateSet(DatePicker view, int year, int monthOfYear,
int dayOfMonth) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
begin.setText(year+"-"+
format(++monthOfYear)+"-"+
format(dayOfMonth));
TimePickerDialog tpg = new TimePickerDialog(MainActivity.this,
new OnTimeSetListener(){
@Override
public void onTimeSet(
TimePicker arg0, int hourOfDay,
int minute) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
begin.setText(begin.getText().toString()
+ " "
+ format(hourOfDay)
+ ":"
+ format(minute)
+ ":" + second);
}},calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY),
calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE), true);
tpg.show();
}
}, calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR),
calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH),
calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
dpg.show();
}
});
//结束时间
end.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
final String second = "00";
DatePickerDialog dpg = new DatePickerDialog(MainActivity.this,
new OnDateSetListener() {
@Override
public void onDateSet(DatePicker view, int year, int monthOfYear,
int dayOfMonth) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
end.setText(year+"-"+
format(++monthOfYear)+"-"+
format(dayOfMonth));
TimePickerDialog tpg = new TimePickerDialog(MainActivity.this,
new OnTimeSetListener(){
@Override
public void onTimeSet(
TimePicker arg0, int hourOfDay,
int minute) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
end.setText(begin.getText().toString()
+ " "
+ format(hourOfDay)
+ ":"
+ format(minute)
+ ":" + second);
}},calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY),
calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE), true);
tpg.show();
}
}, calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR),
calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH),
calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
dpg.show();
}
});
}
/**
* 比较两个时间的大小
* @throws ParseException
*
* */
public static boolean isLarge(String beginTime,String endTime) {
boolean flag = false;
try {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date begin = sdf.parse(beginTime);
Date edn = sdf.parse(endTime);
if(edn.getTime() - begin.getTime() >0){
flag = true;
}else {
flag = false;
}
} catch (ParseException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
return flag;
}
/**
* 在一位数字前加0变成两位数字
*
* @param value
* @return
*/
private String format(int value) {
String s = String.valueOf(value);
if (s.length() == 1) {
s = "0" + s;
}
return s;
}
}
(在F:\java\z自定义dialog+点击弹出时间调整那个\MyDialogTheme)
现在的android手机型号复杂多样,造成了开发过程中使用官方的获取sd卡的方法在部分的手机上并不适用,所以需要进行开发的自己封装,以下就是代码,希望分享出来,大家共同学习
/**
* 获取手机sd卡的工具类
* @author wy
*/
public class SDCardUtils {
/*
* avoid initializations of tool classes
*/
private SDCardUtils() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @Title: getExtSDCardPaths
* @Description: to obtain storage paths, the first path is theoretically
* the returned value of
* Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), namely the
* primary external storage. It can be the storage of internal
* device, or that of external sdcard. If paths.size() >1,
* basically, the current device contains two type of storage:
* one is the storage of the device itself, one is that of
* external sdcard. Additionally, the paths is directory.
* @return List<String>
* @throws IOException
* 获取手机上所有可用的sd卡路径
* @return
*/
public static ArrayList<String> getExtSDCardPaths() {
ArrayList<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();
String extFileStatus = Environment.getExternalStorageState();
File extFile = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();
if (extFileStatus.equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED) && extFile.exists()
&& extFile.isDirectory()) {
paths.add(extFile.getAbsolutePath());
}
try {
// obtain executed result of command line code of 'mount', to judge
// whether tfCard exists by the result
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Process process = runtime.exec("mount");
InputStream is = process.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line = null;
int mountPathIndex = 1;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// format of sdcard file system: vfat/fuse
if ((!line.contains("fat") && !line.contains("fuse") && !line
.contains("storage"))
|| line.contains("secure")
|| line.contains("asec")
|| line.contains("firmware")
|| line.contains("shell")
|| line.contains("obb")
|| line.contains("legacy") || line.contains("data")) {
continue;
}
String[] parts = line.split(" ");
int length = parts.length;
if (mountPathIndex >= length) {
continue;
}
String mountPath = parts[mountPathIndex];
if (!mountPath.contains("/") || mountPath.contains("data")
|| mountPath.contains("Data")) {
continue;
}
File mountRoot = new File(mountPath);
if (!mountRoot.exists() || !mountRoot.isDirectory()) {
continue;
}
boolean equalsToPrimarySD = mountPath.equals(extFile
.getAbsolutePath());
if (equalsToPrimarySD) {
continue;
}
paths.add(mountPath);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return paths;
}
/**
* SD卡剩余空间大小
* @param path 取得SD卡文件路径
* @return 单位MB
*/
public static long getSDFreeSize(String path) {
StatFs sf = new StatFs(path);
// 获取单个数据块的大小(Byte)
long blockSize = sf.getBlockSize();
// 空闲的数据块的数量
long freeBlocks = sf.getAvailableBlocks();
// 返回SD卡空闲大小
return (freeBlocks * blockSize) / 1024 / 1024; //
}
/**
* SD卡总容量
* @param path 取得SD卡文件路径
* @return 单位MB
*/
public static long getSDAllSize(String path) {
StatFs sf = new StatFs(path);
// 获取单个数据块的大小(Byte)
long blockSize = sf.getBlockSize();
// 获取所有数据块数
long allBlocks = sf.getBlockCount();
// 返回SD卡大小
// return allBlocks * blockSize; //单位Byte
// return (allBlocks * blockSize)/1024; //单位KB
return (allBlocks * blockSize) / 1024 / 1024;
}
/**
* 判断当前内存卡是否可用
* @param mContext
* @return
*/
public static final boolean isExist(String sdPath) {
ArrayList<String> list = getExtSDCardPaths();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if(list.contains(sdPath)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
Android手机外置SD卡(TF卡)的获取方法
Android手机上的外置SD卡,起初的时候,即在Android出世的前几年,那时手机的存储是十分有限的,不像现在到处可见16G、32G和64G的存储,因而那时候的手机有的厂商允许插入外置的SD卡,此时这张卡仍处于手机的扩展部分。后来,随着手机的发展以及存储能力的增加,这张外置SD卡,逐渐成为了手机的一部分,不再允许可挺拔了,当然现在依然有的手机允许对存储进行拓展,比如三星等。
那张拓展的存储卡,现在叫做TF卡,且不是所有的手机都支持它,但是有时候有些奇葩需求偏要优先存储在TF卡里面,这叫不得不要求开发人员去检查这张卡是否存在、是否可用。又因为这是手机厂商可拓展、可自定义的部分,所有不同厂商生产的手机,以及同一厂商生产的不同型号的手机,TF卡的位置都相差很大,并没有一个统一的名称或位置。因而这是比较困难的一部分,但是还好Android是开源的,我们可以通过运行时来判断手机是否有TF卡,以及TF卡是否可用。
下面这个方法可以获取手机的可以存储,包括SD卡、TF卡等,对多存储卡进行了匹配,详细的代码如下:
1 public class SDCardScanner {
2 /*
3 * avoid initializations of tool classes
4 */
5 private SDCardScanner() {
6 }
7
8 /**
9 * @Title: getExtSDCardPaths
10 * @Description: to obtain storage paths, the first path is theoretically
11 * the returned value of
12 * Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), namely the
13 * primary external storage. It can be the storage of internal
14 * device, or that of external sdcard. If paths.size() >1,
15 * basically, the current device contains two type of storage:
16 * one is the storage of the device itself, one is that of
17 * external sdcard. Additionally, the paths is directory.
18 * @return List<String>
19 * @throws IOException
20 */
21 public static List<String> getExtSDCardPaths() {
22 List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();
23 String extFileStatus = Environment.getExternalStorageState();
24 File extFile = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();
25 if (extFileStatus.endsWith(Environment.MEDIA_UNMOUNTED)
26 && extFile.exists() && extFile.isDirectory()
27 && extFile.canWrite()) {
28 paths.add(extFile.getAbsolutePath());
29 }
30 try {
31 // obtain executed result of command line code of 'mount', to judge
32 // whether tfCard exists by the result
33 Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
34 Process process = runtime.exec('mount');
35 InputStream is = process.getInputStream();
36 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
37 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
38 String line = null;
39 int mountPathIndex = 1;
40 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
41 // format of sdcard file system: vfat/fuse
42 if ((!line.contains('fat') && !line.contains('fuse') && !line
43 .contains('storage'))
44 || line.contains('secure')
45 || line.contains('asec')
46 || line.contains('firmware')
47 || line.contains('shell')
48 || line.contains('obb')
49 || line.contains('legacy') || line.contains('data')) {
50 continue;
51 }
52 String[] parts = line.split(' ');
53 int length = parts.length;
54 if (mountPathIndex >= length) {
55 continue;
56 }
57 String mountPath = parts[mountPathIndex];
58 if (!mountPath.contains('/') || mountPath.contains('data')
59 || mountPath.contains('Data')) {
60 continue;
61 }
62 File mountRoot = new File(mountPath);
63 if (!mountRoot.exists() || !mountRoot.isDirectory()
64 || !mountRoot.canWrite()) {
65 continue;
66 }
67 boolean equalsToPrimarySD = mountPath.equals(extFile
68 .getAbsolutePath());
69 if (equalsToPrimarySD) {
70 continue;
71 }
72 paths.add(mountPath);
73 }
74 } catch (IOException e) {
75 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
76 e.printStackTrace();
77 }
78 return paths;
79 }
80 }
首先,我把它写成了一个工具类,因而声明了一个私有的构造器,目的就是要防止该类被实例化。
然后,首先获取了Android标准一部分的外置SD卡,如果它可用的话。
然后利用运行时,通过命令行函数'mount'来获取所有的存储位置,并对返回的结果进行SD卡或者TF卡的查找。
最后返回了所有可用于存储的不同的卡的位置,用一个List来保存。由于不是所有的手机都支持TF卡,因而这个List包含的路径未必很多,只有一个SD卡的手机只会返回一个路径,多个可用存储位置的会返回多个路径。
但有一点,是必须的,paths.get(0)肯定是外置SD卡的位置,因为它是primary external storage.
相关文章
- 下面我们来看一篇关于Android子控件超出父控件的范围显示出来方法,希望这篇文章能够帮助到各位朋友,有碰到此问题的朋友可以进来看看哦。 <RelativeLayout xmlns:an...2016-10-02
Android开发中findViewById()函数用法与简化
findViewById方法在android开发中是获取页面控件的值了,有没有发现我们一个页面控件多了会反复研究写findViewById呢,下面我们一起来看它的简化方法。 Android中Fin...2016-09-20- 如果我们的项目需要做来电及短信的功能,那么我们就得在Android模拟器开发这些功能,本来就来告诉我们如何在Android模拟器上模拟来电及来短信的功能。 在Android模拟...2016-09-20
- 夜神android模拟器如何设置代理呢?对于这个问题其实操作起来是非常的简单,下面小编来为各位详细介绍夜神android模拟器设置代理的方法,希望例子能够帮助到各位。 app...2016-09-20
- 为了增强android应用的用户体验,我们可以在一些Button按钮上自定义动态的设置一些样式,比如交互时改变字体、颜色、背景图等。 今天来看一个通过重写Button来动态实...2016-09-20
- 如果我们要在Android应用APP中加载html5页面,我们可以使用WebView,本文我们分享两个WebView加载html5页面实例应用。 实例一:WebView加载html5实现炫酷引导页面大多...2016-09-20
- 关于mysql效率优化一般通过以下两种方式定位执行效率较低的sql语句。通过慢查询日志定位那些执行效率较低的 SQL 语句,用 --log-slow-queries[=file_name] 选项启动时, mysqld 会 写一个包含所有执行时间超过 long_quer...2015-11-08
- 深入理解Android中View和ViewGroup从组成架构上看,似乎ViewGroup在View之上,View需要继承ViewGroup,但实际上不是这样的。View是基类,ViewGroup是它的子类。本教程我们深...2016-09-20
- 下面我们来看一篇关于Android自定义WebView网络视频播放控件开发例子,这个文章写得非常的不错下面给各位共享一下吧。 因为业务需要,以下代码均以Youtube网站在线视...2016-10-02
- 过了这么久,discuz论坛的问题还是困扰着很多网友,其实从各论坛里看到的问题总结出来,很关键的一点都是因为没有将数据表引擎转成InnoDB导致的,discuz在并发稍微高一点的环境下就表现的非常糟糕,产生大量的锁等待,这时候如果...2015-11-24
- java开发的Android应用,性能一直是一个大问题,,或许是Java语言本身比较消耗内存。本文我们来谈谈Android 性能优化之MemoryFile文件读写。 Android匿名共享内存对外A...2016-09-20
- TextView默认是横着显示了,今天我们一起来看看Android设置TextView竖着显示如何来实现吧,今天我们就一起来看看操作细节,具体的如下所示。 在开发Android程序的时候,...2016-10-02
- MySQL是一个功能强大的开源数据库。随着越来越多的数据库驱动的应用程序,人们一直在推动MySQL发展到它的极限。这里是101条调节和优化 MySQL安装的技巧。一些技巧是针对特定的安装环境的,但这些思路是通用的。我已经把...2013-09-11
android.os.BinderProxy cannot be cast to com解决办法
本文章来给大家介绍关于android.os.BinderProxy cannot be cast to com解决办法,希望此文章对各位有帮助呀。 Android在绑定服务的时候出现java.lang.ClassCastExc...2016-09-20- 这篇文章主要介绍了Angular性能优化之第三方组件和懒加载技术,对性能优化感兴趣的同学,可以参考下...2021-05-11
- 这篇文章主要介绍了Android 实现钉钉自动打卡功能的步骤,帮助大家更好的理解和学习使用Android,感兴趣的朋友可以了解下...2021-03-15
- 下面我们来看一篇关于Android 开发之布局细节对比:RTL模式 ,希望这篇文章对各位同学会带来帮助,具体的细节如下介绍。 前言 讲真,好久没写博客了,2016都过了一半了,赶紧...2016-10-02
- 本文给大家介绍的是C#程序优化的小技巧,通过此方法可以有效的降低CPU的占用率,十分的简单实用,有需要的小伙伴可以参考下。...2020-06-25
利用 Chrome Dev Tools 进行页面性能分析的步骤说明(前端性能优化)
这篇文章主要介绍了利用 Chrome Dev Tools 进行页面性能分析的步骤说明(前端性能优化),本文给大家介绍的非常想详细,对大家的学习或工作具有一定的参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下...2021-02-24- 首先如果要在程序中使用sdcard进行存储,我们必须要在AndroidManifset.xml文件进行下面的权限设置: 在AndroidManifest.xml中加入访问SDCard的权限如下: <!--...2016-09-20
