android获取wifi外网ip的方法
android获取wifi外网ip的方法
// 获取外网IP
public static String GetNetIp() {
URL infoUrl = null;
InputStream inStream = null;
try {
// http://iframe.ip138.com/ic.asp
// infoUrl = new URL("http://city.ip138.com/city0.asp");
infoUrl = new URL("http://ip38.com");
URLConnection connection = infoUrl.openConnection();
HttpURLConnection httpConnection = (HttpURLConnection) connection;
int responseCode = httpConnection.getResponseCode();
if (responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) {
inStream = httpConnection.getInputStream();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(inStream, "utf-8"));
StringBuilder strber = new StringBuilder();
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null)
strber.append(line + "\n");
inStream.close();
// 从反馈的结果中提取出IP地址
// int start = strber.indexOf("[");
// Log.d("zph", "" + start);
// int end = strber.indexOf("]", start + 1);
// Log.d("zph", "" + end);
line = strber.substring(378, 395);
line.replaceAll(" ", "");
return line;
}
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
另有一个获取外网IP的高端方法
public static String GetNetIp()
{
String IP = "";
try
{
String address = "http://ip.taobao.com/service/getIpInfo2.php?ip=myip";
URL url = new URL(address);
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url
.openConnection();
connection.setUseCaches(false);
if (connection.getResponseCode() == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK)
{
InputStream in = connection.getInputStream();
// 将流转化为字符串
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(in));
String tmpString = "";
StringBuilder retJSON = new StringBuilder();
while ((tmpString = reader.readLine()) != null)
{
retJSON.append(tmpString + "\n");
}
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(retJSON.toString());
String code = jsonObject.getString("code");
if (code.equals("0"))
{
JSONObject data = jsonObject.getJSONObject("data");
IP = data.getString("ip") + "(" + data.getString("country")
+ data.getString("area") + "区"
+ data.getString("region") + data.getString("city")
+ data.getString("isp") + ")";
Log.e("提示", "您的IP地址是:" + IP);
}
else
{
IP = "";
Log.e("提示", "IP接口异常,无法获取IP地址!");
}
}
else
{
IP = "";
Log.e("提示", "网络连接异常,无法获取IP地址!");
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
IP = "";
Log.e("提示", "获取IP地址时出现异常,异常信息是:" + e.toString());
}
return IP;
}
Android 获取wifi的IP地址
WifiManager wifimanage=(WifiManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);//获取WifiManager
//检查wifi是否开启
if(!wifimanage.isWifiEnabled()) {
wifimanage.setWifiEnabled(true);
}
WifiInfo wifiinfo= wifimanage.getConnectionInfo();
String ip=intToIp(wifiinfo.getIpAddress());
//将获取的int转为真正的ip地址,参考的网上的,修改了下
private String intToIp(int i) {
return (i & 0xFF)+ "." + ((i >> 8 ) & 0xFF)? + "." + ((i >> 16 ) & 0xFF) +"."+((i >> 24 ) & 0xFF );
}
OK,这样就好了吗?呵呵,别忘记加上权限
<uses -permission="" android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE"></uses> <uses -permission="" android:name="adnroid.permission.CHANGE_WIFI_STATE"></use
android开发 获取WIFI和有线的IP地址
首先设置权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE"></uses-permission> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CHANGE_WIFI_STATE"></uses-permission> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WAKE_LOCK"></uses-permission>
/**
* if (intf.getName().toLowerCase().equals("eth0") || intf.getName().toLowerCase().equals("wlan0"))
* 表示:仅过滤无线和有线的ip. networkInterface是有很多的名称的
* 比如sim0,remt1.....等等.我不需要用到就直接过滤了
*
* if (!ipaddress.contains("::"))
* 表示: 过滤掉ipv6的地址.不管无线还是有线 都有这个地址,
* 我这边显示地址大体是:fe80::288:88ff:fe00:1%eth0 fe80::ee17:2fff:fece:c0b4%wlan0
* 一般都是出现在第一次循环.第二次循环就是真正的ipv4的地址.
*
* @return
* @throws SocketException
*/
public String GetIpAddress() throws SocketException {
String ipaddress = "";
Enumeration<NetworkInterface> netInterfaces = null;
try {
netInterfaces = NetworkInterface.getNetworkInterfaces();
while (netInterfaces.hasMoreElements()) {
NetworkInterface intf = netInterfaces.nextElement();
if (intf.getName().toLowerCase().equals("eth0") | | intf.getName().toLowerCase().equals("wlan0")) {
for (Enumeration<InetAddress> enumIpAddr = intf.getInetAddresses(); enumIpAddr.hasMoreElements();) {
InetAddress inetAddress = enumIpAddr.nextElement();
if (!inetAddress.isLoopbackAddress()) {
ipaddress = inetAddress.getHostAddress().toString();
if (!ipaddress.contains("::")) {// ipV6的地址
ipaddress = ipaddress;
}
}
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// final ContentResolver mContentResolver = getContentResolver();
// Settings.System.putInt( mContentResolver,
// Settings.System.WIFI_USE_STATIC_IP, 1);
// Settings.System.putString( mContentResolver,
// Settings.System.WIFI_STATIC_IP, "你的ip地址");
return ipaddress;
}
public String getAddress() {
WifiManager wifiManager = (WifiManager) getActivity().getSystemService(Context.WIFI_SERVICE);
// 判断wifi是否开启
if (!wifiManager.isWifiEnabled()) {
wifiManager.setWifiEnabled(true);
}
WifiInfo wifiInfo = wifiManager.getConnectionInfo();
DhcpInfo info = wifiManager.getDhcpInfo();
int ipAddress = wifiInfo.getIpAddress();
int ii = info.ipAddress;
// return intToIp(ipAddress);
return ipAddress + " dhcp: " + ii;
}
private String intToIp(int i) {
return (i & 0xFF) + "." +
((i >> 8) & 0xFF) + "." +
((i >> 16) & 0xFF) + "." +
(i >> 24 & 0xFF);
}
}如果我们的android应用程序在按键的时候想调用系统的震动服务,我们得先再AndroidMainfest.xml里面加上相应的权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.VIBRATE" />
然后就是
Vibrator vibrator = (Vibrator) getSystemService(VIBRATOR_SERVICE);
// vibrator.vibrate(3000);
// 设置Vibrate的震动周期
vibrator.vibrate(new long[]{1000,2000,3000,4000}, 0);
这里再网上找了个写好的震动的方法类
package com.lxb.switchdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Service;
import android.os.Vibrator;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
/**
* 手机震动工具类
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class VibratorUtil {
/**
* final Activity activity :调用该方法的Activity实例 long milliseconds :震动的时长,单位是毫秒
* long[] pattern :自定义震动模式 。数组中数字的含义依次是[静止时长,震动时长,静止时长,震动时长。。。]时长的单位是毫秒
* boolean isRepeat : 是否反复震动,如果是true,反复震动,如果是false,只震动一次
*/
public static void Vibrate(final Activity activity, long milliseconds) {
Vibrator vib = (Vibrator) activity
.getSystemService(Service.VIBRATOR_SERVICE);
vib.vibrate(milliseconds);
}
public static void Vibrate(final Activity activity, long[] pattern,
boolean isRepeat) {
Vibrator vib = (Vibrator) activity
.getSystemService(Service.VIBRATOR_SERVICE);
vib.vibrate(pattern, isRepeat ? 1 : -1);
}
}
当然在你的activity里面调用的时候只需要在onclick下加上
VibratorUtil.Vibrate(Switch_demoActivity.this, 100);
即可实现简单的震动机制
下来总结下按键声音的机制实现,
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button mButton01;
private SoundPool sp;//声明一个SoundPool
private int music;//定义一个整型用load();来设置suondID
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mButton01=(Button)findViewById(R.id.mButton01);
sp= new SoundPool(10, AudioManager.STREAM_SYSTEM, 5);//第一个参数为同时播放数据流的最大个数,第二数据流类型,第三为声音质量
music = sp.load(this, R.raw.start, 1); //把你的声音素材放到res/raw里,第2个参数即为资源文件,第3个为音乐的优先级
mButton01.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
sp.play(music, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1);
}
}
}
}
raw是在res下面新建文件夹,里面都是不需要编译的可以直接用的资源文件,当然为了避免在有的机器里面不能识别按键声音的问日,最好把需要加载的音频格式转换成ogg格式。
先介绍drawable属性的区别,这个算是比较简单的,但是还是有一点点的小细节需要进行说明,drawable有五个文件夹,分别为hdpi,ldpi,mdpi,xdpi,xxdpi,这五个文件夹想必大家都知道,其实就是为了适应不同分辨率,由于手机分辨率的不同,因此我们的图片需要适应不同手机的分辨率...hdpi:480x800 mdpi:480x320 ldpi:320x240xdpi:1280x720 xxdpi 1920x1280其实这个数字并不是非常精确的,只是说明每一个阶段都有一个分辨率范围...Android由于和IOS不一样,IOS是不需要考虑分辨率的,但是Android必须要考虑分辨率问题,比如说我们在hdpi中放入的图片在布局中显示是非常正常的,但是在xdpi里,那就会变得非常的小...因此我们在设计app的时候,我们需要考虑不同的手机,因此我们需要在这几个文件夹中分别放入不同大小的图片,这样Andorid系统可以根据手机的分辨率来选择合适的图片资源进行加载,收一下dip到底表示的是什么意思,Android中表示大小的一个单位,dpi指像素/英寸,简单的说一下dpi到底表示的大小值...ldpi指120,mdpi指160,hdpi 指240,xhdpi指320。比如说小米手机是4英寸、854×480的分辨率,那么小米手机的dpi就是854的平方加480的平方和开2次方后除以4,结果大约是245。如果应用安装在小米手机上,那么系统会调用图中drawable-hdpi里面的资源。这样,你只要做4套资源分别放在 drawable-ldpi、drawable-mdpi、drawable-hdpi以及drawable-xdpi下(图标可以按照3:4:6:8的 比例制作图片资源),那么就可以图片在不同分辨率上有可能失真的情况...
Android中LinearLayout布局技巧
上面只是一个小小的介绍一下,下面来说一下最近发现了一种布局的技巧,原本个人认为RelativeLayout是最好用的布局,同时自己也在使用着表格布局,但是发现使用TableLayout已经是很少很少了,没想到还有一种布局方式是LinearLayout,有人会问,LinearLayout有什么稀奇的,其实LinearLayout并不稀奇,而是这里有一个属性是layout_weight,这样是我最近才发现的...虽然很早就有了...总之我觉得这个东西是非常好用的,通过使用0dp+layout_weight来进行布局是非常巧妙的一种方式...其实就是实现了比例布局..这样布局就可以直接适应不同手机的屏幕...从而避免了在不同手机上布局无法同步的问题..举个例子...
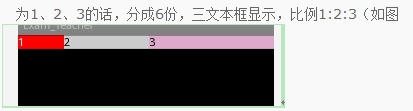
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#0045f5" android:gravity="center" android:text="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#00ff47" android:gravity="center" android:text="2" android:layout_weight="1"/> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#ff5600" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="3" /> </LinearLayout>
这个就是布局后的样式,我们设置的layout_width=“wrap_content”,按照常理来说,系统应该会为三个TextView分配默认的空间,并且三个空间的大小应该是相同的,但是正是因为我们为后面两个设置了layout_weight属性,这样系统会先为第一个TextView分配默认空间大小,就比如说10dp吧,假设我们的屏幕大小为480x800的分辨率,那么剩下470dp的大小将会按照比例分配给两个TextView...第二个TextView分配到的大小就是(470/2=225dp),第二个也是225dp...
那么我们是否就可以做出一个结论呢?就是设置了layout_weight后的控件,会按指定比例分配剩余控件呢?其实并不是这样的,我们再来看一个布局...
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#0045f5" android:gravity="center" android:text="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#00ff47" android:gravity="center" android:text="2222222222222222222" android:layout_weight="1"/> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#ff5600" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="3" /> </LinearLayout>

这个就是布局的结果,这样就会出现问题了,其实在设置了wrap_content,系统会先看控件到底要占用多少空间,就是先回按照wrap_content对控件分配空间,由于第二个控件的默认空间比较大,因此系统只能使用wrap_content对其分配空间,不会再按照layout_weight属性按照比例分配空间了...因此这里我们设置layout_width的时候不能设置为wrap_content,我们需要设置成0dp....再看下面的例子....
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" > <TextView android:layout_width="0dip" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#0045f5" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="0dip" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#00ff47" android:gravity="center" android:text="2222222222222222222" android:layout_weight="2"/> <TextView android:layout_width="0dip" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#ff5600" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="3" android:text="3" /> </LinearLayout>

这里我们把layout_width=“0dp”,然后配合layout_weight属性,实现了空间宽度的1:2:3的进行分配,而长度由于我们没有进行规定,因此使用了wrap_content属性...这样0dp配合着layout_weight属性实现了布局的比例分配...那么如果我们想要把高度也按照比例分配的话,那么就把layout_height=“0dp”...然后配合weight属性就可以同样实现了布局中高度按照比例进行分配...这里我们一定要使用0dp...解释一下Android如何会按照比例布局呢?我们仍然假设我们的屏幕大小是480,那么由于我们设置的三个TextView大小都为0dp,那么系统会先按照我们设置的大小进行计算,480-3*0=480,那么剩余的空间大小仍然为480dp,最后剩余的空间按照比例来进行分配...这样就实现了宽度的1:2:3的大小进行分配...如果我们使用了“fill_parent”属性,那么就会出现不相同的效果...在看下面的布局...
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="horizontal" > <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#0045f5" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#00ff47" android:gravity="center" android:text="2" android:layout_weight="2"/> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#ff5600" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="2" android:text="3" /> </LinearLayout>

这就是我们使用了fill_parent的后果,并没有按照我们想要的比例出现结果...这里导致的问题就是,由于我们设置的空间大小都为fill_parent属性,因此剩余空间大小就是480-3*480=-960dp,然后按照比例进行分配大小 480+(-960*(1/5))=228dp 480*(-960*(2/5))=96dp 第三个也是96dp...这样反而导致成了3:1:1的情况出现...这就是使用了fill_parent属性出现的问题...使用fill_parent这个属性配合layout_weight属性,分配的比例是需要我们人为进行计算...看到这里,是不是已经清晰了呢?
Android:LinearLayout布局中Layout_weight的深刻理解
首先看一下LinearLayout布局中Layout_weight属性的作用:它是用来分配属于空间的一个属性,你可以设置他的权重。很多人不知道剩余空间是个什么概念,下面我先来说说剩余空间。
看下面代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="left" android:text="one"/> <EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1.0" android:text="two"/> <EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="right" android:text="three"/> </LinearLayout>
运行结果是:
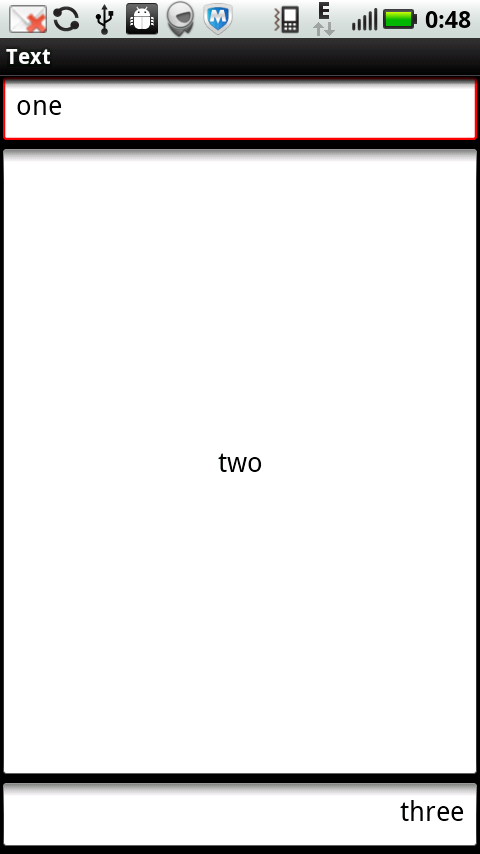
看上面代码:只有Button2使用了Layout_weight属性,并赋值为了1,而Button1和Button3没有设置Layout_weight这个属性,根据API,可知,他们默认是0
下面我就来讲,Layout_weight这个属性的真正的意思:Android系统先按照你设置的3个Button高度Layout_height值wrap_content,给你分配好他们3个的高度,
然后会把剩下来的屏幕空间全部赋给Button2,因为只有他的权重值是1,这也是为什么Button2占了那么大的一块空间。
有了以上的理解我们就可以对网上关于Layout_weight这个属性更让人费解的效果有一个清晰的认识了。
我们来看这段代码:
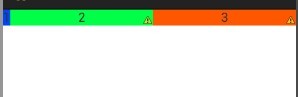
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <TextView android:background="#ff0000" android:layout_width="**" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="1" android:textColor="@android:color/white" android:layout_weight="1"/> <TextView android:background="#cccccc" android:layout_width="**" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="2" android:textColor="@android:color/black" android:layout_weight="2" /> <TextView android:background="#ddaacc" android:layout_width="**" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="3" android:textColor="@android:color/black" android:layout_weight="3" /> </LinearLayout>
三个文本框的都是 layout_width=“wrap_content ”时,会得到以下效果
按照上面的理解,系统先给3个TextView分配他们的宽度值wrap_content(宽度足以包含他们的内容1,2,3即可),然后会把剩下来的屏幕空间按照1:2:3的比列分配给3个textview,所以就出现了上面的图像。
而当layout_width=“fill_parent”时,如果分别给三个TextView设置他们的Layout_weight为1、2、2的话,就会出现下面的效果:

你会发现1的权重小,反而分的多了,这是为什么呢???网上很多人说是当layout_width=“fill_parent”时,weighth值越小权重越大,优先级越高,就好像在背口诀
一样,其实他们并没有真正理解这个问题,真正的原因是Layout_width="fill_parent"的原因造成的。依照上面理解我们来分析:
系统先给3个textview分配他们所要的宽度fill_parent,也就是说每一都是填满他的父控件,这里就死屏幕的宽度
那么这时候的剩余空间=1个parent_width-3个parent_width=-2个parent_width (parent_width指的是屏幕宽度 )
那么第一个TextView的实际所占宽度应该=fill_parent的宽度,即parent_width + 他所占剩余空间的权重比列1/5 * 剩余空间大小(-2 parent_width)=3/5parent_width
同理第二个TextView的实际所占宽度=parent_width + 2/5*(-2parent_width)=1/5parent_width;
第三个TextView的实际所占宽度=parent_width + 2/5*(-2parent_width)=1/5parent_width;所以就是3:1:1的比列显示了。
这样你也就会明白为什么当你把三个Layout_weight设置为1、2、3的话,会出现下面的效果了:

第三个直接不显示了,为什么呢?一起来按上面方法算一下吧:
系统先给3个textview分配他们所要的宽度fill_parent,也就是说每一都是填满他的父控件,这里就死屏幕的宽度
那么这时候的剩余空间=1个parent_width-3个parent_width=-2个parent_width (parent_width指的是屏幕宽度 )
那么第一个TextView的实际所占宽度应该=fill_parent的宽度,即parent_width + 他所占剩余空间的权重比列1/6 * 剩余空间大小(-2 parent_width)=2/3parent_width
同理第二个TextView的实际所占宽度=parent_width + 2/6*(-2parent_width)=1/3parent_width;
第三个TextView的实际所占宽度=parent_width + 3/6*(-2parent_width)=0parent_width;所以就是2:1:0的比列显示了。第三个就直接没有空间了。
实现方法一代码
1、准备AIDL文件
挂断电话的AIDL文件都是Android自带的文件,我们可以从Android的源代码中找到这两个文件,它们分别是NeighboringCellInfo.aidl和ITelephony.aidl
我把NeighboringCellInfo.aidl放在项目的android.telephony包下,将ITelephony.aidl放在com.android.internal.telephony包下
NeighboringCellInfo.aid具体内容如下:
/* //device/java/android/android/content/Intent.aidl ** ** Copyright 2007, The Android Open Source Project ** ** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); ** you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. ** You may obtain a copy of the License at ** ** http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 ** ** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software ** distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, ** WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. ** See the License for the specific language governing permissions and ** limitations under the License. */ package android.telephony; parcelable NeighboringCellInfo;
ITelephony.aidl具体内容如下:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2007 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.android.internal.telephony;
import android.os.Bundle;
import java.util.List;
import android.telephony.NeighboringCellInfo;
/**
* Interface used to interact with the phone. Mostly this is used by the
* TelephonyManager class. A few places are still using this directly.
* Please clean them up if possible and use TelephonyManager insteadl.
*
* {@hide}
*/
interface ITelephony {
/**
* Dial a number. This doesn't place the call. It displays
* the Dialer screen.
* @param number the number to be dialed. If null, this
* would display the Dialer screen with no number pre-filled.
*/
void dial(String number);
/**
* Place a call to the specified number.
* @param number the number to be called.
*/
void call(String number);
/**
* If there is currently a call in progress, show the call screen.
* The DTMF dialpad may or may not be visible initially, depending on
* whether it was up when the user last exited the InCallScreen.
*
* @return true if the call screen was shown.
*/
boolean showCallScreen();
/**
* Variation of showCallScreen() that also specifies whether the
* DTMF dialpad should be initially visible when the InCallScreen
* comes up.
*
* @param showDialpad if true, make the dialpad visible initially,
* otherwise hide the dialpad initially.
* @return true if the call screen was shown.
*
* @see showCallScreen
*/
boolean showCallScreenWithDialpad(boolean showDialpad);
/**
* End call or go to the Home screen
*
* @return whether it hung up
*/
boolean endCall();
/**
* Answer the currently-ringing call.
*
* If there's already a current active call, that call will be
* automatically put on hold. If both lines are currently in use, the
* current active call will be ended.
*
* TODO: provide a flag to let the caller specify what policy to use
* if both lines are in use. (The current behavior is hardwired to
* "answer incoming, end ongoing", which is how the CALL button
* is specced to behave.)
*
* TODO: this should be a oneway call (especially since it's called
* directly from the key queue thread).
*/
void answerRingingCall();
/**
* Silence the ringer if an incoming call is currently ringing.
* (If vibrating, stop the vibrator also.)
*
* It's safe to call this if the ringer has already been silenced, or
* even if there's no incoming call. (If so, this method will do nothing.)
*
* TODO: this should be a oneway call too (see above).
* (Actually *all* the methods here that return void can
* probably be oneway.)
*/
void silenceRinger();
/**
* Check if we are in either an active or holding call
* @return true if the phone state is OFFHOOK.
*/
boolean isOffhook();
/**
* Check if an incoming phone call is ringing or call waiting.
* @return true if the phone state is RINGING.
*/
boolean isRinging();
/**
* Check if the phone is idle.
* @return true if the phone state is IDLE.
*/
boolean isIdle();
/**
* Check to see if the radio is on or not.
* @return returns true if the radio is on.
*/
boolean isRadioOn();
/**
* Check if the SIM pin lock is enabled.
* @return true if the SIM pin lock is enabled.
*/
boolean isSimPinEnabled();
/**
* Cancels the missed calls notification.
*/
void cancelMissedCallsNotification();
/**
* Supply a pin to unlock the SIM. Blocks until a result is determined.
* @param pin The pin to check.
* @return whether the operation was a success.
*/
boolean supplyPin(String pin);
/**
* Handles PIN MMI commands (PIN/PIN2/PUK/PUK2), which are initiated
* without SEND (so <code>dial</code> is not appropriate).
*
* @param dialString the MMI command to be executed.
* @return true if MMI command is executed.
*/
boolean handlePinMmi(String dialString);
/**
* Toggles the radio on or off.
*/
void toggleRadioOnOff();
/**
* Set the radio to on or off
*/
boolean setRadio(boolean turnOn);
/**
* Request to update location information in service state
*/
void updateServiceLocation();
/**
* Enable location update notifications.
*/
void enableLocationUpdates();
/**
* Disable location update notifications.
*/
void disableLocationUpdates();
/**
* Enable a specific APN type.
*/
int enableApnType(String type);
/**
* Disable a specific APN type.
*/
int disableApnType(String type);
/**
* Allow mobile data connections.
*/
boolean enableDataConnectivity();
/**
* Disallow mobile data connections.
*/
boolean disableDataConnectivity();
/**
* Report whether data connectivity is possible.
*/
boolean isDataConnectivityPossible();
Bundle getCellLocation();
/**
* Returns the neighboring cell information of the device.
*/
List<NeighboringCellInfo> getNeighboringCellInfo();
int getCallState();
int getDataActivity();
int getDataState();
/**
* Returns the current active phone type as integer.
* Returns TelephonyManager.PHONE_TYPE_CDMA if RILConstants.CDMA_PHONE
* and TelephonyManager.PHONE_TYPE_GSM if RILConstants.GSM_PHONE
*/
int getActivePhoneType();
/**
* Returns the CDMA ERI icon index to display
*/
int getCdmaEriIconIndex();
/**
* Returns the CDMA ERI icon mode,
* 0 - ON
* 1 - FLASHING
*/
int getCdmaEriIconMode();
/**
* Returns the CDMA ERI text,
*/
String getCdmaEriText();
/**
* Returns true if CDMA provisioning needs to run.
*/
boolean getCdmaNeedsProvisioning();
/**
* Returns the unread count of voicemails
*/
int getVoiceMessageCount();
/**
* Returns the network type
*/
int getNetworkType();
/**
* Return true if an ICC card is present
*/
boolean hasIccCard();
}
准备好文件后,会在项目的gen目录下自动生成与两个文件所在包一样的包,同时会自动生成ITelephony.java文件
如下图:
2、新建PhoneUtils类,并写一个方法endCall()
这个方法就是挂断电话的方法,具体实现如下
//挂断电话
public void endCall(String incomingNumber){
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("android.os.ServiceManager");
Method method = clazz.getMethod("getService", String.class);
IBinder ibinder = (IBinder) method.invoke(null, Context.TELEPHONY_SERVICE);
ITelephony iTelephony = ITelephony.Stub.asInterface(ibinder);
iTelephony.endCall();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStrackTrace();
}
}
3、注册权限
最后别忘了在AndroidManifest.xml文件中注册权限
具体实现如下:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CALL_PHONE"/>
实现方法二代码
Android自动挂断电话
android的新版本已经把Phone类给隐藏起来了,想要用代码实现挂断电话,就必须通过AIDL才行,
第一步:在程序中新建一个包,包名必须为:com.android.internal.telephony,因为要使用aidl,
第二步:在这个包里面新建一个名为ITelephony.aidl的文件,然后在文件里面写入代码:
package com.android.internal.telephony;
interface ITelephony{
boolean endCall();
void answerRingingCall();
}然后保存,eclipse会自动在gen文件夹下生成一个ITelephony.java的类。
主程序的代码如下:
package ling.Phonemanager;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.telephony.PhoneStateListener;
import android.telephony.TelephonyManager;
import com.android.internal.telephony.ITelephony;
public class Phonemanager extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
private ITelephony iTelephony;
private TelephonyManager manager;
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
phoner();
manager.listen(new PhoneStateListener(){
@Override
public void onCallStateChanged(int state, String incomingNumber) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCallStateChanged(state, incomingNumber);
switch(state){
//判断是否有电话接入
case 1:
try {
//当电话接入时,自动挂断。
iTelephony.endCall();
System.out.println("uncall");
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}, PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_CALL_STATE);
}
public void phoner(){
manager = (TelephonyManager)getSystemService(TELEPHONY_SERVICE);
Class <TelephonyManager> c = TelephonyManager.class;
Method getITelephonyMethod = null;
try {
getITelephonyMethod = c.getDeclaredMethod("getITelephony", (Class[])null);
getITelephonyMethod.setAccessible(true);
iTelephony = (ITelephony) getITelephonyMethod.invoke(manager, (Object[])null);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}只要在电话接入时,再加上一个判断电话号码是否是黑名单的功能,就可以做成一个黑名单的程序了,获取电话号码的函数是:getLine1Number();
仿下载助手界面效果
线程池 ThreadPoolExecutor
在下面介绍实现下载原理的时候,我想尝试倒着来说,这样是否好理解一点?
我们都知道,下载助手,比如360, 百度的 手机助手,下载APP 的时候 ,都可以同时下载多个,所以,下载肯定是多线程的,所以我们就需要一个线程工具类 来管理我们的线程,这个工具类的核心,就是 线程池。
线程池ThreadPoolExecutor ,先简单学习下这个线程池的使用
/**
* Parameters:
corePoolSize
the number of threads to keep in the pool, even if they are idle, unless allowCoreThreadTimeOut is set
maximumPoolSize
the maximum number of threads to allow in the pool
keepAliveTime
when the number of threads is greater than the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads will wait for new tasks before terminating.
unit
the time unit for the keepAliveTime argument
workQueue
the queue to use for holding tasks before they are executed. This queue will hold only the Runnable tasks submitted by the execute method.
handler
the handler to use when execution is blocked because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
Throws:
IllegalArgumentException - if one of the following holds:
corePoolSize < 0
keepAliveTime < 0
maximumPoolSize <= 0
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize
NullPointerException - if workQueue or handler is null
*/
ThreadPoolExecutor threadpool=new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, handler)
上面是 ThreadPoolExecutor的参数介绍,
第一个参数 corePoolSize : 空闲时 存在的线程数目、
第二个参数 maximumPoolSize :允许同时存在的最大线程数、
第三个参数 keepAliveTime: 这个参数是 允许空闲线程存活的时间、
第四个参数 unit : 是 时间的单位 、
第五个参数 workQueue :这个是一个容器,它里面存放的是、 threadpool.execute(new Runnable()) 执行的线程.new Runnable()、
第六个参数 handler:当执行被阻塞时,该处理程序将被阻塞,因为线程的边界和队列容量达到了 。
工具类 ThreadManager
介绍完了 线程池参数,那我们就先创建一个线程管理的工具类 ThreadManager
public class ThreadManager {
public static final String DEFAULT_SINGLE_POOL_NAME = "DEFAULT_SINGLE_POOL_NAME";
private static ThreadPoolProxy mLongPool = null;
private static Object mLongLock = new Object();
private static ThreadPoolProxy mShortPool = null;
private static Object mShortLock = new Object();
private static ThreadPoolProxy mDownloadPool = null;
private static Object mDownloadLock = new Object();
private static Map<String, ThreadPoolProxy> mMap = new HashMap<String, ThreadPoolProxy>();
private static Object mSingleLock = new Object();
/** 获取下载线程 */
public static ThreadPoolProxy getDownloadPool() {
synchronized (mDownloadLock) {
if (mDownloadPool == null) {
mDownloadPool = new ThreadPoolProxy(3, 3, 5L);
}
return mDownloadPool;
}
}
/** 获取一个用于执行长耗时任务的线程池,避免和短耗时任务处在同一个队列而阻塞了重要的短耗时任务,通常用来联网操作 */
public static ThreadPoolProxy getLongPool() {
synchronized (mLongLock) {
if (mLongPool == null) {
mLongPool = new ThreadPoolProxy(5, 5, 5L);
}
return mLongPool;
}
}
/** 获取一个用于执行短耗时任务的线程池,避免因为和耗时长的任务处在同一个队列而长时间得不到执行,通常用来执行本地的IO/SQL */
public static ThreadPoolProxy getShortPool() {
synchronized (mShortLock) {
if (mShortPool == null) {
mShortPool = new ThreadPoolProxy(2, 2, 5L);
}
return mShortPool;
}
}
/** 获取一个单线程池,所有任务将会被按照加入的顺序执行,免除了同步开销的问题 */
public static ThreadPoolProxy getSinglePool() {
return getSinglePool(DEFAULT_SINGLE_POOL_NAME);
}
/** 获取一个单线程池,所有任务将会被按照加入的顺序执行,免除了同步开销的问题 */
public static ThreadPoolProxy getSinglePool(String name) {
synchronized (mSingleLock) {
ThreadPoolProxy singlePool = mMap.get(name);
if (singlePool == null) {
singlePool = new ThreadPoolProxy(1, 1, 5L);
mMap.put(name, singlePool);
}
return singlePool;
}
}
public static class ThreadPoolProxy {
private ThreadPoolExecutor mPool;
private int mCorePoolSize;
private int mMaximumPoolSize;
private long mKeepAliveTime;
private ThreadPoolProxy(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime) {
mCorePoolSize = corePoolSize;
mMaximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
mKeepAliveTime = keepAliveTime;
}
/** 执行任务,当线程池处于关闭,将会重新创建新的线程池 */
public synchronized void execute(Runnable run) {
if (run == null) {
return;
}
if (mPool == null || mPool.isShutdown()) {
mPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(mCorePoolSize, mMaximumPoolSize, mKeepAliveTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new AbortPolicy());
}
mPool.execute(run);
}
/** 取消线程池中某个还未执行的任务 */
public synchronized void cancel(Runnable run) {
if (mPool != null && (!mPool.isShutdown() || mPool.isTerminating())) {
mPool.getQueue().remove(run);
}
}
/** 取消线程池中某个还未执行的任务 */
public synchronized boolean contains(Runnable run) {
if (mPool != null && (!mPool.isShutdown() || mPool.isTerminating())) {
return mPool.getQueue().contains(run);
} else {
return false;
}
}
/** 立刻关闭线程池,并且正在执行的任务也将会被中断 */
public void stop() {
if (mPool != null && (!mPool.isShutdown() || mPool.isTerminating())) {
mPool.shutdownNow();
}
}
/** 平缓关闭单任务线程池,但是会确保所有已经加入的任务都将会被执行完毕才关闭 */
public synchronized void shutdown() {
if (mPool != null && (!mPool.isShutdown() || mPool.isTerminating())) {
mPool.shutdownNow();
}
}
}
}
这个线程池工具类 主要就是 生成一个线程池, 以及 取消线程池中的任务,查询线程池中是否包含某一任务。
下载任务 DownloadTask
我们的现在线程 DownloadTask 就 通过 ThreadManager .getDownloadPool().execute() 方法 交给线程池去管理。
有了线程池管理我们的线程, 那我们下一步 就是 DownloadTask 这个类去下载了。
/** 下载任务 */
public class DownloadTask implements Runnable {
private DownloadInfo info;
public DownloadTask(DownloadInfo info) {
this.info = info;
}
@Override
public void run() {
info.setDownloadState(STATE_DOWNLOADING);// 先改变下载状态
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
File file = new File(info.getPath());// 获取下载文件
HttpResult httpResult = null;
InputStream stream = null;
if (info.getCurrentSize() == 0 || !file.exists()
|| file.length() != info.getCurrentSize()) {
// 如果文件不存在,或者进度为0,或者进度和文件长度不相符,就需要重新下载
info.setCurrentSize(0);
file.delete();
}
httpResult = HttpHelper.download(info.getUrl());
// else {
// // //文件存在且长度和进度相等,采用断点下载
// httpResult = HttpHelper.download(info.getUrl() + "&range=" +
// info.getCurrentSize());
// }
if (httpResult == null
|| (stream = httpResult.getInputStream()) == null) {
info.setDownloadState(STATE_ERROR);// 没有下载内容返回,修改为错误状态
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
} else {
try {
skipBytesFromStream(stream, info.getCurrentSize());
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true);
int count = -1;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while (((count = stream.read(buffer)) != -1)
&& info.getDownloadState() == STATE_DOWNLOADING) {
// 每次读取到数据后,都需要判断是否为下载状态,如果不是,下载需要终止,如果是,则刷新进度
fos.write(buffer, 0, count);
fos.flush();
info.setCurrentSize(info.getCurrentSize() + count);
notifyDownloadProgressed(info);// 刷新进度
}
} catch (Exception e) {
info.setDownloadState(STATE_ERROR);
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
info.setCurrentSize(0);
file.delete();
} finally {
IOUtils.close(fos);
if (httpResult != null) {
httpResult.close();
}
}
// 判断进度是否和app总长度相等
if (info.getCurrentSize() == info.getAppSize()) {
info.setDownloadState(STATE_DOWNLOADED);
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
} else if (info.getDownloadState() == STATE_PAUSED) {// 判断状态
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
} else {
info.setDownloadState(STATE_ERROR);
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
info.setCurrentSize(0);// 错误状态需要删除文件
file.delete();
}
}
mTaskMap.remove(info.getId());
}
}
下载的原理 很简单,就是 通过 目标的URL 拿到流,然后写到本地。
因为下载在 run() 里面执行,这个DownloadTask 类 我们就看run() 方法的实现,所以 关键代码 就是下面一点点
fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true);
int count = -1;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while (((count = stream.read(buffer)) != -1)
&& info.getDownloadState() == STATE_DOWNLOADING) {
// 每次读取到数据后,都需要判断是否为下载状态,如果不是,下载需要终止,如果是,则刷新进度
fos.write(buffer, 0, count);
fos.flush();
info.setCurrentSize(info.getCurrentSize() + count);
notifyDownloadProgressed(info);// 刷新进度
}
这个在我们刚接触Java 的时候 肯定都写过了。 这就是往本地写数据的代码。所以run()方法中的 前面 就是拿到 stream 输入流, 以及 把file 创建出来。
刷新进度,状态
关于控制 button中text 显示 暂停 ,下载,还是进度,就靠 notifyDownloadProgressed(info);和 notifyDownloadStateChanged(info)两个方法, 这两个方法 实际上调用的是两个接口,只要我们在我们需要改变界面的类里 实现这两个接口,就可以接收到 包含最新信息的info对象。而我们在哪个类里改变button 上面 显示的文字呢? 当然是在 我们的adapter 里面了,大家都知道 是在 adapter 的getView() 方法里面 加载的每一条数据的布局。
那就一起看下是不是这样子呢?
public class RecommendAdapter extends BaseAdapter implements
DownloadManager.DownloadObserver {
ArrayList<AppInfo> list;
private List<ViewHolder> mDisplayedHolders;
private FinalBitmap finalBitmap;
private Context context;
public RecommendAdapter(ArrayList<AppInfo> list, FinalBitmap finalBitmap,
Context context) {
this.list = list;
this.context = context;
this.finalBitmap = finalBitmap;
mDisplayedHolders = new ArrayList<ViewHolder>();
}
public void startObserver() {
DownloadManager.getInstance().registerObserver(this);
}
public void stopObserver() {
DownloadManager.getInstance().unRegisterObserver(this);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return list.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return list.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
final AppInfo appInfo = list.get(position);
final ViewHolder holder;
if (convertView == null) {
holder = new ViewHolder(context);
} else {
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
holder.setData(appInfo);
mDisplayedHolders.add(holder);
return holder.getRootView();
}
@Override
public void onDownloadStateChanged(DownloadInfo info) {
refreshHolder(info);
}
@Override
public void onDownloadProgressed(DownloadInfo info) {
refreshHolder(info);
}
public List<ViewHolder> getDisplayedHolders() {
synchronized (mDisplayedHolders) {
return new ArrayList<ViewHolder>(mDisplayedHolders);
}
}
public void clearAllItem() {
if (list != null){
list.clear();
}
if (mDisplayedHolders != null) {
mDisplayedHolders.clear();
}
}
public void addItems(ArrayList<AppInfo> infos) {
list.addAll(infos);
}
private void refreshHolder(final DownloadInfo info) {
List<ViewHolder> displayedHolders = getDisplayedHolders();
for (int i = 0; i < displayedHolders.size(); i++) {
final ViewHolder holder = displayedHolders.get(i);
AppInfo appInfo = holder.getData();
if (appInfo.getId() == info.getId()) {
AppUtil.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
holder.refreshState(info.getDownloadState(),
info.getProgress());
}
});
}
}
}
public class ViewHolder {
public TextView textView01;
public TextView textView02;
public TextView textView03;
public TextView textView04;
public ImageView imageView_icon;
public Button button;
public LinearLayout linearLayout;
public AppInfo mData;
private DownloadManager mDownloadManager;
private int mState;
private float mProgress;
protected View mRootView;
private Context context;
private boolean hasAttached;
public ViewHolder(Context context) {
mRootView = initView();
mRootView.setTag(this);
this.context = context;
}
public View getRootView() {
return mRootView;
}
public View initView() {
View view = AppUtil.inflate(R.layout.item_recommend_award);
imageView_icon = (ImageView) view
.findViewById(R.id.imageview_task_app_cion);
textView01 = (TextView) view
.findViewById(R.id.textview_task_app_name);
textView02 = (TextView) view
.findViewById(R.id.textview_task_app_size);
textView03 = (TextView) view
.findViewById(R.id.textview_task_app_desc);
textView04 = (TextView) view
.findViewById(R.id.textview_task_app_love);
button = (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.button_task_download);
linearLayout = (LinearLayout) view
.findViewById(R.id.linearlayout_task);
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
System.out.println("mState:173 "+mState);
if (mState == DownloadManager.STATE_NONE
|| mState == DownloadManager.STATE_PAUSED
|| mState == DownloadManager.STATE_ERROR) {
mDownloadManager.download(mData);
} else if (mState == DownloadManager.STATE_WAITING
|| mState == DownloadManager.STATE_DOWNLOADING) {
mDownloadManager.pause(mData);
} else if (mState == DownloadManager.STATE_DOWNLOADED) {
// tell2Server();
mDownloadManager.install(mData);
}
}
});
return view;
}
public void setData(AppInfo data) {
if (mDownloadManager == null) {
mDownloadManager = DownloadManager.getInstance();
}
String filepath= FileUtil.getDownloadDir(AppUtil.getContext()) + File.separator + data.getName() + ".apk";
boolean existsFile = FileUtil.isExistsFile(filepath);
if(existsFile){
int fileSize = FileUtil.getFileSize(filepath);
if(data.getSize()==fileSize){
DownloadInfo downloadInfo = DownloadInfo.clone(data);
downloadInfo.setCurrentSize(data.getSize());
downloadInfo.setHasFinished(true);
mDownloadManager.setDownloadInfo(data.getId(),downloadInfo );
}
// else if(fileSize>0){
// DownloadInfo downloadInfo = DownloadInfo.clone(data);
// downloadInfo.setCurrentSize(data.getSize());
// downloadInfo.setHasFinished(false);
// mDownloadManager.setDownloadInfo(data.getId(),downloadInfo );
// }
}
DownloadInfo downloadInfo = mDownloadManager.getDownloadInfo(data
.getId());
if (downloadInfo != null) {
mState = downloadInfo.getDownloadState();
mProgress = downloadInfo.getProgress();
} else {
mState = DownloadManager.STATE_NONE;
mProgress = 0;
}
this.mData = data;
refreshView();
}
public AppInfo getData() {
return mData;
}
public void refreshView() {
linearLayout.removeAllViews();
AppInfo info = getData();
textView01.setText(info.getName());
textView02.setText(FileUtil.FormetFileSize(info.getSize()));
textView03.setText(info.getDes());
textView04.setText(info.getDownloadNum() + "下载量);
finalBitmap.display(imageView_icon, info.getIconUrl());
if (info.getType().equals("0")) {
// mState = DownloadManager.STATE_READ;
textView02.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}else{
String path=FileUtil.getDownloadDir(AppUtil.getContext()) + File.separator + info.getName() + ".apk";
hasAttached = FileUtil.isValidAttach(path, false);
DownloadInfo downloadInfo = mDownloadManager.getDownloadInfo(info
.getId());
if (downloadInfo != null && hasAttached) {
if(downloadInfo.isHasFinished()){
mState = DownloadManager.STATE_DOWNLOADED;
}else{
mState = DownloadManager.STATE_PAUSED;
}
} else {
mState = DownloadManager.STATE_NONE;
if(downloadInfo !=null){
downloadInfo.setDownloadState(mState);
}
}
}
refreshState(mState, mProgress);
}
public void refreshState(int state, float progress) {
mState = state;
mProgress = progress;
switch (mState) {
case DownloadManager.STATE_NONE:
button.setText(R.string.app_state_download);
break;
case DownloadManager.STATE_PAUSED:
button.setText(R.string.app_state_paused);
break;
case DownloadManager.STATE_ERROR:
button.setText(R.string.app_state_error);
break;
case DownloadManager.STATE_WAITING:
button.setText(R.string.app_state_waiting);
break;
case DownloadManager.STATE_DOWNLOADING:
button.setText((int) (mProgress * 100) + "%");
break;
case DownloadManager.STATE_DOWNLOADED:
button.setText(R.string.app_state_downloaded);
break;
// case DownloadManager.STATE_READ:
// button.setText(R.string.app_state_read);
// break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
何时 注册 监听observer
里面代码有点多,那就看startObserver()方法做了什么。
public void startObserver() {
DownloadManager.getInstance().registerObserver(this);
}
这里 是 注册了observer, Observer 是什么东西?在DownloadManager 中我们定义了
public interface DownloadObserver {
public void onDownloadStateChanged(DownloadInfo info);
public void onDownloadProgressed(DownloadInfo info);
}
一个接口,里面有两个抽象方法 一个是 进度,另一个是下载状态。
那回过头来,屡一下, 我们在 下载的关键代码里面调用了 DownloadObserver onDownloadProgressed() DownloadObserver.onDownloadStateChanged()两个抽象方法,而我们在 adapter
@Override
public void onDownloadStateChanged(DownloadInfo info) {
refreshHolder(info);
}
@Override
public void onDownloadProgressed(DownloadInfo info) {
refreshHolder(info);
}
中实现了 这两个方法 就可以轻松的控制 去 刷新 和改变 下载状态了。
细心的朋友 或许 发现问题了,对,我们还没有注册Observer,就在 DownloadManager 中去调用了。
这里 在看下DownloadManager 中 调用的方法
/** 当下载状态发送改变的时候回调 */
public void notifyDownloadStateChanged(DownloadInfo info) {
synchronized (mObservers) {
for (DownloadObserver observer : mObservers) {
observer.onDownloadStateChanged(info);
}
}
}
/** 当下载进度发送改变的时候回调 */
public void notifyDownloadProgressed(DownloadInfo info) {
synchronized (mObservers) {
for (DownloadObserver observer : mObservers) {
observer.onDownloadProgressed(info);
}
}
}
是的,这里我们遍历一个observer 容器,然后去刷新 ,所以我们还需要 把 Observer 对象 添加到 集合 mObservers 中,
所以肯定有这样一个方法 讲 observer 添加到集合中 。
/* 注册观察者 /
public void registerObserver(DownloadObserver observer) {
synchronized (mObservers) {
if (!mObservers.contains(observer)) {
mObservers.add(observer);
}
}
}
/** 反注册观察者 */
public void unRegisterObserver(DownloadObserver observer) {
synchronized (mObservers) {
if (mObservers.contains(observer)) {
mObservers.remove(observer);
}
}
}
所以最后一步,因为 adapter 方法中有 startObserver, 所以 我们在 主界面 MainActivity 的类中调用 adapter.startObser() 将 实现了 接口的adapter 对象 添加到 Observer 容器中 就可以了。
OK。大功告成!
=============================================
DownloadManager 代码
这里 贴一下DownloadManager 代码
public class DownloadManager {
public static final int STATE_NONE = 0;
/** 等待中 */
public static final int STATE_WAITING = 1;
/** 下载中 */
public static final int STATE_DOWNLOADING = 2;
/** 暂停 */
public static final int STATE_PAUSED = 3;
/** 下载完毕 */
public static final int STATE_DOWNLOADED = 4;
/** 下载失败 */
public static final int STATE_ERROR = 5;
// public static final int STATE_READ = 6;
private static DownloadManager instance;
private DownloadManager() {
}
/** 用于记录下载信息,如果是正式项目,需要持久化保存 */
private Map<Long, DownloadInfo> mDownloadMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<Long, DownloadInfo>();
/** 用于记录观察者,当信息发送了改变,需要通知他们 */
private List<DownloadObserver> mObservers = new ArrayList<DownloadObserver>();
/** 用于记录所有下载的任务,方便在取消下载时,通过id能找到该任务进行删除 */
private Map<Long, DownloadTask> mTaskMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<Long, DownloadTask>();
public static synchronized DownloadManager getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new DownloadManager();
}
return instance;
}
/** 注册观察者 */
public void registerObserver(DownloadObserver observer) {
synchronized (mObservers) {
if (!mObservers.contains(observer)) {
mObservers.add(observer);
}
}
}
/** 反注册观察者 */
public void unRegisterObserver(DownloadObserver observer) {
synchronized (mObservers) {
if (mObservers.contains(observer)) {
mObservers.remove(observer);
}
}
}
/** 当下载状态发送改变的时候回调 */
public void notifyDownloadStateChanged(DownloadInfo info) {
synchronized (mObservers) {
for (DownloadObserver observer : mObservers) {
observer.onDownloadStateChanged(info);
}
}
}
/** 当下载进度发送改变的时候回调 */
public void notifyDownloadProgressed(DownloadInfo info) {
synchronized (mObservers) {
for (DownloadObserver observer : mObservers) {
observer.onDownloadProgressed(info);
}
}
}
/** 下载,需要传入一个appInfo对象 */
public synchronized void download(AppInfo appInfo) {
// 先判断是否有这个app的下载信息
DownloadInfo info = mDownloadMap.get(appInfo.getId());
if (info == null) {// 如果没有,则根据appInfo创建一个新的下载信息
info = DownloadInfo.clone(appInfo);
mDownloadMap.put(appInfo.getId(), info);
}
// 判断状态是否为STATE_NONE、STATE_PAUSED、STATE_ERROR。只有这3种状态才能进行下载,其他状态不予处理
if (info.getDownloadState() == STATE_NONE
|| info.getDownloadState() == STATE_PAUSED
|| info.getDownloadState() == STATE_ERROR) {
// 下载之前,把状态设置为STATE_WAITING,因为此时并没有产开始下载,只是把任务放入了线程池中,当任务真正开始执行时,才会改为STATE_DOWNLOADING
info.setDownloadState(STATE_WAITING);
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);// 每次状态发生改变,都需要回调该方法通知所有观察者
DownloadTask task = new DownloadTask(info);// 创建一个下载任务,放入线程池
mTaskMap.put(info.getId(), task);
ThreadManager.getDownloadPool().execute(task);
}
}
/** 暂停下载 */
public synchronized void pause(AppInfo appInfo) {
stopDownload(appInfo);
DownloadInfo info = mDownloadMap.get(appInfo.getId());// 找出下载信息
if (info != null) {// 修改下载状态
info.setDownloadState(STATE_PAUSED);
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
}
}
/** 取消下载,逻辑和暂停类似,只是需要删除已下载的文件 */
public synchronized void cancel(AppInfo appInfo) {
stopDownload(appInfo);
DownloadInfo info = mDownloadMap.get(appInfo.getId());// 找出下载信息
if (info != null) {// 修改下载状态并删除文件
info.setDownloadState(STATE_NONE);
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
info.setCurrentSize(0);
File file = new File(info.getPath());
file.delete();
}
}
/** 安装应用 */
public synchronized void install(AppInfo appInfo) {
stopDownload(appInfo);
DownloadInfo info = mDownloadMap.get(appInfo.getId());// 找出下载信息
if (info != null) {// 发送安装的意图
Intent installIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
installIntent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
installIntent.setDataAndType(Uri.parse("file://" + info.getPath()),
"application/vnd.android.package-archive");
AppUtil.getContext().startActivity(installIntent);
}
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
}
/** 启动应用,启动应用是最后一个 */
public synchronized void open(AppInfo appInfo) {
try {
Context context = AppUtil.getContext();
// 获取启动Intent
Intent intent = context.getPackageManager()
.getLaunchIntentForPackage(appInfo.getPackageName());
context.startActivity(intent);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
/** 如果该下载任务还处于线程池中,且没有执行,先从线程池中移除 */
private void stopDownload(AppInfo appInfo) {
DownloadTask task = mTaskMap.remove(appInfo.getId());// 先从集合中找出下载任务
if (task != null) {
ThreadManager.getDownloadPool().cancel(task);// 然后从线程池中移除
}
}
/** 获取下载信息 */
public synchronized DownloadInfo getDownloadInfo(long id) {
return mDownloadMap.get(id);
}
public synchronized void setDownloadInfo(long id, DownloadInfo info) {
mDownloadMap.put(id, info);
}
/** 下载任务 */
public class DownloadTask implements Runnable {
private DownloadInfo info;
public DownloadTask(DownloadInfo info) {
this.info = info;
}
@Override
public void run() {
info.setDownloadState(STATE_DOWNLOADING);// 先改变下载状态
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
File file = new File(info.getPath());// 获取下载文件
HttpResult httpResult = null;
InputStream stream = null;
if (info.getCurrentSize() == 0 || !file.exists()
|| file.length() != info.getCurrentSize()) {
// 如果文件不存在,或者进度为0,或者进度和文件长度不相符,就需要重新下载
info.setCurrentSize(0);
file.delete();
}
httpResult = HttpHelper.download(info.getUrl());
// else {
// // //文件存在且长度和进度相等,采用断点下载
// httpResult = HttpHelper.download(info.getUrl() + "&range=" +
// info.getCurrentSize());
// }
if (httpResult == null
|| (stream = httpResult.getInputStream()) == null) {
info.setDownloadState(STATE_ERROR);// 没有下载内容返回,修改为错误状态
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
} else {
try {
skipBytesFromStream(stream, info.getCurrentSize());
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true);
int count = -1;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while (((count = stream.read(buffer)) != -1)
&& info.getDownloadState() == STATE_DOWNLOADING) {
// 每次读取到数据后,都需要判断是否为下载状态,如果不是,下载需要终止,如果是,则刷新进度
fos.write(buffer, 0, count);
fos.flush();
info.setCurrentSize(info.getCurrentSize() + count);
notifyDownloadProgressed(info);// 刷新进度
}
} catch (Exception e) {
info.setDownloadState(STATE_ERROR);
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
info.setCurrentSize(0);
file.delete();
} finally {
IOUtils.close(fos);
if (httpResult != null) {
httpResult.close();
}
}
// 判断进度是否和app总长度相等
if (info.getCurrentSize() == info.getAppSize()) {
info.setDownloadState(STATE_DOWNLOADED);
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
} else if (info.getDownloadState() == STATE_PAUSED) {// 判断状态
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
} else {
info.setDownloadState(STATE_ERROR);
notifyDownloadStateChanged(info);
info.setCurrentSize(0);// 错误状态需要删除文件
file.delete();
}
}
mTaskMap.remove(info.getId());
}
}
public interface DownloadObserver {
public abstract void onDownloadStateChanged(DownloadInfo info);
public abstract void onDownloadProgressed(DownloadInfo info);
}
/* 重写了Inpustream 中的skip(long n) 方法,将数据流中起始的n 个字节跳过 */
private long skipBytesFromStream(InputStream inputStream, long n) {
long remaining = n;
// SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE is used to determine the size of skipBuffer
int SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE = 10000;
// skipBuffer is initialized in skip(long), if needed.
byte[] skipBuffer = null;
int nr = 0;
if (skipBuffer == null) {
skipBuffer = new byte[SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE];
}
byte[] localSkipBuffer = skipBuffer;
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
while (remaining > 0) {
try {
long skip = inputStream.skip(10000);
nr = inputStream.read(localSkipBuffer, 0,
(int) Math.min(SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE, remaining));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (nr < 0) {
break;
}
remaining -= nr;
}
return n - remaining;
}
}
有两点 需要说明,关于 点击暂停后,再继续下载 有两种方式可以实现
第一种 点击暂停的时候 记录下载了 多少,然后 再点击 继续下载 时,告诉服务器, 让服务器接着 上次的数据 往本地传递,
代码 就是 我们 DownloadTask 下载时候,判断一下
// //文件存在且长度和进度相等,采用断点下载
httpResult = HttpHelper.download(info.getUrl() + "&range=" + info.getCurrentSize());
通过 range 来区分 当前的下载size.
服务器 处理的代码 也很简单 就是一句话
String range = req.getParameter(“range”); 拿到 range 判断 range 存在不存在。
如果不存在
FileInputStream stream = new FileInputStream(file);
int count = -1;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while ((count = stream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
SystemClock.sleep(20);
out.write(buffer, 0, count);
out.flush();
}
stream.close();
out.close();
如果存在 那么跳过range 个字节
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
raf.seek(Long.valueOf(range));
int count = -1;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while ((count = raf.read(buffer)) != -1) {
SystemClock.sleep(10);
out.write(buffer, 0, count);
out.flush();
}
raf.close();
out.close();
另一种方式是本地处理,这个demo 中就是本地处理的, 但是有一个问题, 因为 Java api的原因 ,inputStream.skip() 方法 并不能准确的 跳过多少个字节,
而是 小于你想要跳过的字节,所以 你要去遍历 一直到 满足你要跳过的字节 在继续写, 因为 这样的方法有一个缺点,就是在下载很大的文件,
比如文件大小20M ,当已经下载了15M 此时你去暂停,在继续下载,那么要跳过前面的15M 将会话费很多时间。
所以这个仅限于学习。实际中 如果要下载大的文件,不能用这种方法。
Android 之多线程下载原理
在Android之中呢,对于多线程的操作很是平凡,所以对于多线程的理解越深,那么对于自己的程序便能够很好的运行
这也是对于Android开发是一个重要的知识点,那么我们现在来了解多线程的下载原理。
android 多线程下载
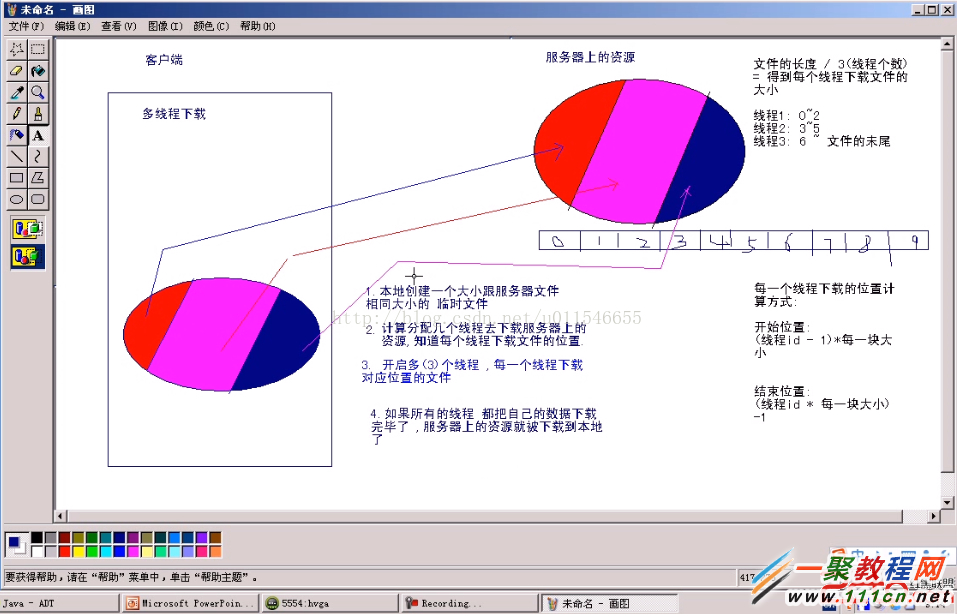
多线程下载步骤: 1.本地创建一个跟服务器一样的大小一样的文件 临时文件。 2.计算分配几个线程去下载服务器上的资源 每个文件下载的位置。 3.开启线程,每一个线程下载对应的文件。 4.如果所有的线程都把自己的数据下载完成了,服务器上的资源就被下载到本地了
如图所示:(假设有三个线程在进行下载)
vcq9Cr+qyrzOu9bDo7oKo6jP37PMaWQgLSAxo6kgKiDDv9K7uPa/7LXEtPPQoQq94cr4zrvWw6O6IAqjqM/fs8xpZKOpKiDDv9K7v+y1xLTz0KEgLSAxCjxicj4KCs/Cw+ajrM7Sw8fPyNPDamF2YbT6wuvAtMq1z9bSu8/CCnBhY2thZ2UgY29tLnplbmd0YW8uZGVtbzs8YnI+Cjxicj4KPGJyPgppbXBvcnQgamF2YS5pby5JbnB1dFN0cmVhbTs8YnI+CmltcG9ydCBqYXZhLmlvLlJhbmRvbUFjY2Vzc0ZpbGU7PGJyPgppbXBvcnQgamF2YS5uZXQuSHR0cFVSTENvbm5lY3Rpb247PGJyPgppbXBvcnQgamF2YS5uZXQuVVJMOzxicj4KPGJyPgo8YnI+CnB1YmxpYyBjbGFzcyBEZW1vTG9hZGVyIHs8YnI+CnByaXZhdGUgc3RhdGljIERlbW9Mb2FkZXIgbG9hZGVyID0gbmV3IERlbW9Mb2FkZXIoKTs8YnI+CnByaXZhdGUgc3RhdGljIGludCB0aHJlYWRDb3VudCA9IDM7PGJyPgo8YnI+Cjxicj4KcHJpdmF0ZSBEZW1vTG9hZGVyKCkgezxicj4KPGJyPgo8YnI+Cn08YnI+Cjxicj4KLy8gtaXA/cnovMbEo8q9PGJyPgpwdWJsaWMgc3RhdGljIERlbW9Mb2FkZXIgZ2V0SW5zdGFuY2UoKSB7PGJyPgpyZXR1cm4gbG9hZGVyOzxicj4KfTxicj4KPGJyPgo8YnI+CnB1YmxpYyB2b2lkIGRvd25GaWxlKFN0cmluZyBwYXRoKSB7PGJyPgovLyDIpbf+zvHG97bLu/HIoc7EvP61xLOktsgs1NqxvrXYtLS9qNK7uPa4+rf+zvHG99K70fm089ChtcTOxLz+PGJyPgp0cnkgezxicj4KVVJMIHVybCA9IG5ldyBVUkwocGF0aCk7PGJyPgpIdHRwVVJMQ29ubmVjdGlvbiBjb25uZWN0aW9uID0gKEh0dHBVUkxDb25uZWN0aW9uKSB1cmw8YnI+Ci5vcGVuQ29ubmVjdGlvbigpOzxicj4KY29ubmVjdGlvbi5zZXREb0lucHV0KHRydWUpOzxicj4KY29ubmVjdGlvbi5zZXRSZXF1ZXN0TWV0aG9kKA=="GET");
connection.setReadTimeout(5000);
int code = connection.getResponseCode();
if (code == 200) {
// 获取服务器端文件的长度
int fileLength = connection.getContentLength();
// 本地创建一个跟服务器一样大小的文件
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("setup.ext", "rwd");
raf.setLength(fileLength);
raf.close();
// 假设三个线程下载
int blockSize = fileLength / threadCount;
for (int threadId = 0; threadId < threadCount; threadId++) {
int startIndex = (threadId - 1) * blockSize;
int endIndex = threadId * blockSize - 1;
if (threadId == threadCount) {
endIndex = fileLength;
}
System.out.println("线程:" + threadId + ",下载:" + startIndex
+ "--->" + endIndex);
// 开始下载
new DownLoadThread(threadId, startIndex, endIndex, path)
.start();
}
System.out.println("文件总长度为:" + fileLength);
} else {
System.out.println("请求失败!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 下载文件的主线程
*
* @author Administrator zengtao
*
*/
public class DownLoadThread extends Thread {
private int threadId;
private int startIndex;
private int endIndex;
private String path;
/**
*
* @param threadId
* 线程id
* @param startIndex
* 线程下载开始位置
* @param endIndex
* 线程下载结束位置
* @param path
* 线程下载结束文件放置地址
*/
public DownLoadThread(int threadId, int startIndex, int endIndex,
String path) {
super();
this.threadId = threadId;
this.startIndex = startIndex;
this.endIndex = endIndex;
this.path = path;
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
URL url;
try {
url = new URL(path);
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url
.openConnection();
// 请求服务器下载部分的文件,制定开始的位置,和结束位置
connection.setRequestProperty("Range", "bytes=" + startIndex
+ "-" + endIndex);
connection.setDoInput(true);
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");
connection.setReadTimeout(5000);
// 从服务器获取的全部数据,返回:200,从服务器获取部分数据,返回:206
int code = connection.getResponseCode();
System.out.println("code = " + code);
InputStream is = connection.getInputStream();
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("setup.exe", "rwd");
// 随机写文件的时候,从什么时候开始
raf.seek(startIndex);
int len = 0;
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
while ((len = is.read(buff)) != -1) {
raf.write(buff, 0, len);
}
is.close();
raf.close();
System.out.println("线程:" + threadId + ",下载完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
要使用该类的时候,只需要知道一个url地址,然后调用里面的downFile()方法,就会开始下载文件了,这样实现可以下载一个安装包,比如:在网上下载一个qq,微信等的安装包,自己安装到电脑上,便可以用该方法实现。
相关文章
- 下面本文章来给大家介绍在php中成员变量的一些对比了,文章举了四个例子在这例子中分别对不同成员变量进行测试与获取操作,下面一起来看看。 有如下4个代码示例,你认...2016-11-25
php 中file_get_contents超时问题的解决方法
file_get_contents超时我知道最多的原因就是你机器访问远程机器过慢,导致php脚本超时了,但也有其它很多原因,下面我来总结file_get_contents超时问题的解决方法总结。...2016-11-25- php 获取用户IP与IE信息程序 function onlineip() { global $_SERVER; if(getenv('HTTP_CLIENT_IP')) { $onlineip = getenv('HTTP_CLIENT_IP');...2016-11-25
- php如何实现抓取网页图片,相较于手动的粘贴复制,使用小程序要方便快捷多了,喜欢编程的人总会喜欢制作一些简单有用的小软件,最近就参考了网上一个php抓取图片代码,封装了一个php远程抓取图片的类,测试了一下,效果还不错分享...2015-10-30
- php获取一个文件夹的mtime的程序了,这个就是时间问题了,对于这个问题我们来看小编整理的几个例子,具体的操作例子如下所示。 php很容易获取到一个文件夹的mtime,可以...2016-11-25
- 相信很多站长都遇到过这样一个问题,访问页面时出现408错误,下面一聚教程网将为大家介绍408错误出现的原因以及408错误的解决办法。 HTTP 408错误出现原因: HTT...2017-01-22
- 下面我们来看一篇关于Android子控件超出父控件的范围显示出来方法,希望这篇文章能够帮助到各位朋友,有碰到此问题的朋友可以进来看看哦。 <RelativeLayout xmlns:an...2016-10-02
- ps软件是现在非常受大家喜欢的一款软件,有着非常不错的使用功能。这次文章就给大家介绍下ps把文字背景变透明的操作方法,喜欢的一起来看看。 1、使用Photoshop软件...2017-07-06
- 获取网站icon,常用最简单的方法就是通过website/favicon.ico来获取,不过由于很多网站都是在页面里面设置favicon,所以此方法很多情况都不可用。 更好的办法是通过google提供的服务来实现:http://www.google.com/s2/favi...2014-06-07
- 1.在没有设置默认值的情况下: 复制代码 代码如下:SELECT userinfo.id, user_name, role, adm_regionid, region_name , create_timeFROM userinfoLEFT JOIN region ON userinfo.adm_regionid = region.id 结果:...2014-05-31
intellij idea快速查看当前类中的所有方法(推荐)
这篇文章主要介绍了intellij idea快速查看当前类中的所有方法,本文通过实例代码给大家介绍的非常详细,对大家的学习或工作具有一定的参考借鉴价值,需要的朋友可以参考下...2020-09-02js导出table数据到excel即导出为EXCEL文档的方法
复制代码 代码如下: <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <meta ht...2013-10-13- 批量更新mysql更新语句很简单,更新一条数据的某个字段,一般这样写:复制代码 代码如下:UPDATE mytable SET myfield = 'value' WHERE other_field = 'other_value';如果更新同一字段为同一个值,mysql也很简单,修改下where即...2013-10-04
- ps软件是一款非常不错的图片处理软件,有着非常不错的使用效果。这次文章要给大家介绍的是ps怎么制作倒影,一起来看看设计倒影的方法。 用ps怎么做倒影最终效果̳...2017-07-06
- 主要功能:获取浏览器显示区域(可视区域)的高度 : $(window).height(); 获取浏览器显示区域(可视区域)的宽度 :$(window).width(); 获取页面的文档高度 $(document).height(); 获取页面的文档宽度 :$(document).width();...2015-10-21
- 本文涉及的主题虽然很基础,在许多人看来属于小伎俩,但在JavaScript基础知识中属于一个综合性的话题。这里会涉及到对象属性的封装、原型、构造函数、闭包以及立即执行表达式等知识。公有方法 公有方法就是能被外部访问...2015-11-08
安卓手机wifi打不开修复教程,安卓手机wifi打不开解决方法
手机wifi打不开?让小编来告诉你如何解决。还不知道的朋友快来看看。 手机wifi是现在生活中最常用的手机功能,但是遇到手机wifi打不开的情况该怎么办呢?如果手机wifi...2016-12-21- 最近想自学PHP ,做了个验证码,但不知道怎么搞的,总出现一个如下图的小红叉,但验证码就是显示不出来,原因如下 未修改之前,出现如下错误; (1)修改步骤如下,原因如下,原因是apache权限没开, (2)点击打开php.int., 搜索extension=ph...2013-10-04
Android开发中findViewById()函数用法与简化
findViewById方法在android开发中是获取页面控件的值了,有没有发现我们一个页面控件多了会反复研究写findViewById呢,下面我们一起来看它的简化方法。 Android中Fin...2016-09-20- 单个字符分割 string s="abcdeabcdeabcde"; string[] sArray=s.Split('c'); foreach(string i in sArray) Console.WriteLine(i.ToString()); 输出下面的结果: ab de...2020-06-25
